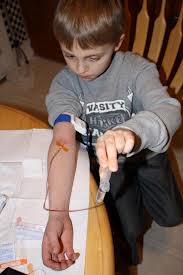
نشانه های تشخیص در هموفیلی A و B یکسان هستند :
- کبودی های بزرگ
- خونریزی داخلی در عضلات و مفاصل
- خونریزی خودبخودی ( خونریزی ناگهانی داخلی بدون هیچ دلیل موجه و روشنی )
- خونریزی طولانی مدت پس از کشیدن دندان و عمل جراحی
- خونریزی طولانی مدت پس از تصادف و بویژه در ناحیه سر و گردن که بسیار خطرناکترند
خونریزی داخلی عضلات و مفاصل و علائم آن
- احساس مورمور شدن
- تورم
- درد و سفتی عضلات
- مشکل در حرکت دادن عضو خونریزی دهنده
خونریزی در کجاها رخ می دهند؟
خونریزی در افراد هموفیلی می تواند داخلی یا خارجی باشد .
شایع ترین خونریزی داخلی عضلانی در افراد مبتلا به هموفیلی در عضلات بازو و ساعد و عضله جلوی کشاله ران (Iliopsoas) و عضله چهارسر ران می باشد و شایع ترین خونریزی های داخلی مفصلی در مفاصل زانو ، مچ پا و آرنج رخ می دهد .
اگر خونریزی ها بطور مکرر در یک مفصل رخ دهد میتواند موجب آسیب های شدید و در پی آن دردناک شدن آن مفصل شود .
خونریزی های مکرر می توانند موجب مشکلات دیگری مانند آرتریت شوند . این می تواند باعث شود که بیمار در انجام فعالیت های ساده و یا راه رفتن دچار مشکل شود . با این حال معمولاً مفاصل دست در بیماران هموفیلی کمتر از مفاصل اندام تحتانی دچار آرتریت می شوند .
هموفیلی چگونه تشخیص داده می شود؟
هموفیلی با نمونه گیری از خون و اندازه گیری سطح فعالیت فاکتور در آن تشخیص داده می شود . هموفیلی A با تست سطح فعالیت فاکتور ۸ و هموفیلی B با اندازه گیری سطح فعالیت فاکتور ۹ تشخیص داده می شود .
اگر مادر حامله مشکوک به ناقل بودن بیماری هموفیلی باشد ، قبل از تولد کودک می توان تست های تشخیصی را انجام داد . تشخیص پیش از تولد را می توان در ۹ تا ۱۱ هفتگی به روش نمونه گیری از پرزهای جفتی (CVS) یا به روش نمونه گیری خون جنین در مرحله پس از ۱۸ هفتگی انجام داد .
آزمایش های ذکر شده در این بخش را می توان از طریق مشاوره در یک مرکز درمانی هموفیلی در سراسر جهان انجام داد .
The signs of hemophilia A and B are the same:
- Big bruises
- Bleeding into muscles and joints
- Spontaneous bleeding (sudden bleeding inside the body for no clear reason)
- Prolonged bleeding after getting a cut, removing a tooth, or having surgery.
- Bleeding for a long time after an accident, especially after an injury to the head.
Bleeding into a joint or muscle causes:
- an ache or “funny feeling”
- swelling
- pain and stiffness
- difficulty using a joint or muscle
Where does bleeding occur?
People with hemophilia can bleed inside or outside the body. Most bleeding in hemophilia occurs internally, into the muscles or joints. The most common muscle bleeds occur in the muscles of the upper arm and forearm, the iliopsoas muscle (the front of the groin area), the thigh, and the calf. The joints that are most often affected are the knee, ankle, and elbow.
If bleeding occurs many times into the same joint, the joint can become damaged and painful.
Repeated bleeding can cause other health problems like arthritis. This can make it difficult to walk or do simple activities. However, the joints of the hands are not usually affected in hemophilia (unlike some kinds of arthritis).
How is hemophilia diagnosed?
Hemophilia is diagnosed by taking a blood sample and measuring the level of factor activity in the blood. Hemophilia A is diagnosed by testing the level of factor VIII activity. Hemophilia B is diagnosed by measuring the level of factor IX activity.
If the mother is a known carrier of hemophilia, testing can be done before a baby is born. Prenatal diagnosis can be done at 9 to 11 weeks by chorionic villus sampling (CVS) or by fetal blood sampling at a later stage (18 or more weeks).
These tests can be done at a hemophilia treatment centre. Consult the Global Treatment Centre Directory for information on treatment centres around the world.
به نقل از وبسایت فدراسیون جهانی هموفیلی :
http://www.wfh.org/en/page.aspx?pid=640
بازدید: 583


 ۷ مهر ۱۳۹۴
۷ مهر ۱۳۹۴
 نوشته شده توسط مدیر سایت
نوشته شده توسط مدیر سایت